Is there a need to work with data stored in a database (DB) using a different application?
In such cases, one approach is to first extract the DB data into a CSV file and then read that CSV file from the other application.
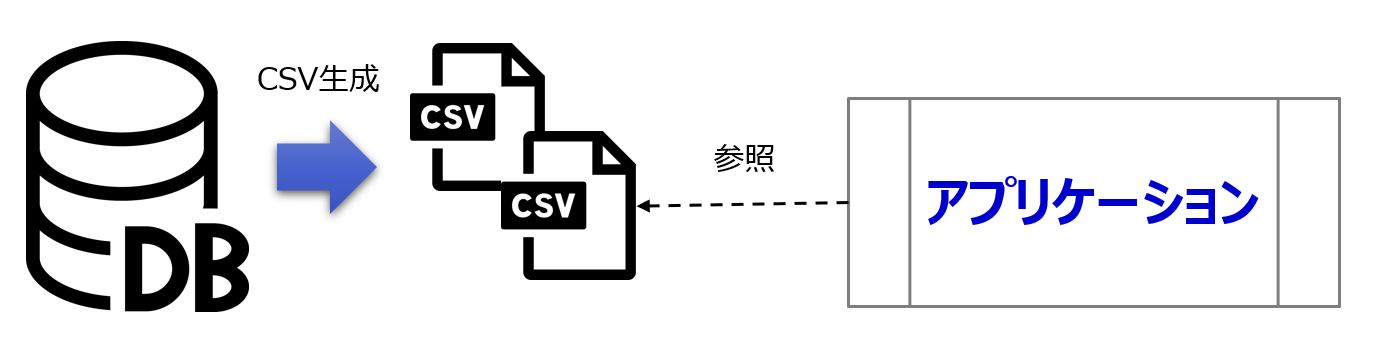
This time, we will explain a program that uses VBS to save data extracted from an Oracle DB into a CSV file.
The source code can be downloaded from here: ↓
template-vbs/ExportCsvOracle/
Program Workflow
Although the program's main purpose is to save data extracted from a DB into a CSV file, the general workflow is as follows:
① Load necessary configuration information.
↓
② Connect to the Oracle DB.
↓
③ Execute SQL containing the SELECT statement.
↓
④ Save the executed SQL result to a CSV file.
↓
⑤ Disconnect from the Oracle DB.Package Structure
The program's functionality isn't contained within a single source file. It involves a folder and file structure, as shown below:
ExportCsvOracle/
├csv/
├sql/
├Config.ini
└ExportCsvOracle.vbs| Folder/File | Description |
|---|---|
| ExportCsvOracle.vbs | Execution program. |
| Config.ini | Configuration information for DB connections and folder paths. |
| sql (Folder) | Contains files storing the SELECT statements. |
| csv (Folder) | Stores CSV files extracted from the DB. |
Explanation of Source Code
For program execution, configuration information will be loaded from an INI file.
▼ Config.ini
[source_db]
provider=OraOLEDB.Oracle
data_source=TESTDB
user_id=system
password=sys
[path]
sql_folder=sql
csv_folder=csvThe INI file in this case contains the following information:
- Connection information to the DB (Oracle)
- Folder name (path) for storing SQL statements
- Folder name (path) for storing generated CSV files
This information from the INI file is read and stored in variables within the VBS script for later use. For more details on this process, you can refer to a separate article: VBS | Getting Data from an INI File
Connecting to the Oracle DB
In this section, we prepare functions necessary for various operations with the Oracle DB.
' ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
' brief: Connect to the DB (Oracle)
' note :
' ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
Sub OpenDBOracle(ByRef objAdoCon, provider, dataSource, user, pass)
If DEBUG_MODE = 1 Then
WScript.Echo "Connecting to the DB."
End If
Dim constr
Set objAdoCon = WScript.CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
constr = "Provider=" & provider & ";Data Source=" & dataSource _
& ";User ID=" & user & ";Password=" & pass
If DEBUG_MODE = 1 Then
WScript.Echo constr
End If
objAdoCon.ConnectionString = constr
objAdoCon.Open
If DEBUG_MODE = 1 Then
WScript.Echo "Connected to the DB."
End If
End Sub
' ... (Other DB-related functions)In this context, we will only be using the DB connection and disconnection functions.
You can utilize the variables read from the earlier INI file to perform DB operations like this:
Dim objAdoCon ' ADO connection
' 1. Connect to the DB
OpenDBOracle objAdoCon, SDB_PROVIDER, SDB_DATA_SOURCE, SDB_USER, SDB_PASS
...
...
...
' 4. Disconnect from the DB
CloseDB objAdoCon
Set objAdoCon = NothingExecuting SQL Statements
Now that we have established a connection to the Oracle DB, let's proceed to explain how to execute SQL statements and retrieve record sets. The workflow for this section is as follows:
Retrieve SQL files from the SQL storage folder ※ One SELECT statement per SQL file
↓
Extract SQL statements from SQL files
↓
Execute SQL statements and retrieve record sets
First, we will prepare functions needed for each step:
' ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
' brief: Execute SQL SELECT statement and retrieve record set
' note : Return -> Record Set
' ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
Function ExcuteSQLgetRS(objAdoCon, strSQL)
Dim objAdoRS ' Record Set
Set objAdoRS = objAdoCon.Execute(strSQL)
Set ExcuteSQLgetRS = objAdoRS ' Remember to use Set for objects
End Function
' ... (Other functions)With these functions, you can proceed to execute SQL statements and retrieve record sets. Though I'll skip detailed explanations, the record set will contain information from the extraction result specified in the SQL SELECT statement.
You can call these functions within your main program code:
Dim objAdoCon ' ADO connection
Dim strSQLFiles ' SQL file collection to execute
Dim strSQLFile ' SQL file to execute
Dim strSQL ' SQL to execute
Dim objAdoRS ' ADO record set
Dim csvText ' CSV text obtained from SELECT query
' 1. Connect to the DB
OpenDBOracle objAdoCon, SDB_PROVIDER, SDB_DATA_SOURCE, SDB_USER, SDB_PASS
' 2. Read SQL file collection
strSQLFiles = GetFileNames(SQL_FOLDER_PATH)
' 3. CSV generation
For Each strSQLFile In strSQLFiles ' Iterate through each SQL file
strSQL = GetFileText(strSQLFile) ' Retrieve the SQL statement
Set objAdoRS = ExcuteSQLgetRS(objAdoCon, strSQL) ' Execute the SQL statement and get the record set
csvText = GetCSVTextFromRS(objAdoRS) ' Convert the record set to CSV-formatted text
WriteFile CSV_FOLDER_PATH & "\" & GetBaseName(strSQLFile), csvText, "csv" ' Generate CSV file
NextThis completes the creation of CSV files.
Saving Executed SQL Results to CSV Files
Until now, the SQL results have been stored in a record set. However, to save the data in CSV format, you need to convert the record set into a text format compatible with CSV.
The workflow here is as follows
:
① Convert the record set to CSV (text)
↓
② Write the converted text to a CSV file
' ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
' brief: Convert record set to CSV
' note : Return -> CSV-formatted text
' ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
Function GetCSVTextFromRS(ByRef objAdoRS)
Dim csvText
Dim i
csvText = ""
Do While objAdoRS.EOF <> True
For i = 0 to objAdoRS.fields.count -1
If i <> objAdoRS.fields.count -1 then
csvText = csvText & objAdoRS(i).value & ", "
Else
csvText = csvText & objAdoRS(i).value
End If
Next
csvText = csvText & vbCrLf
objAdoRS.MoveNext
Loop
objAdoRS.Close
Set objAdoRS = Nothing
If DEBUG_MODE = 1 Then
WScript.Echo csvText
End If
GetCSVTextFromRS = csvText
End Function
' ... (Other functions)You can incorporate these functions into your main program by adding the following code:
Dim objAdoCon ' ADO connection
Dim strSQLFiles ' SQL file collection to execute
Dim strSQLFile ' SQL file to execute
Dim strSQL ' SQL to execute
Dim objAdoRS ' ADO record set
Dim csvText ' CSV text obtained from SELECT query
' 1. Connect to the DB
OpenDBOracle objAdoCon, SDB_PROVIDER, SDB_DATA_SOURCE, SDB_USER, SDB_PASS
' 2. Read SQL file collection
strSQLFiles = GetFileNames(SQL_FOLDER_PATH)
' 3. CSV generation
For Each strSQLFile In strSQLFiles ' Iterate through each SQL file
strSQL = GetFileText(strSQLFile) ' Retrieve the SQL statement
Set objAdoRS = ExcuteSQLgetRS(objAdoCon, strSQL) ' Execute the SQL statement and get the record set
csvText = GetCSVTextFromRS(objAdoRS) ' Convert the record set to CSV-formatted text
WriteFile CSV_FOLDER_PATH & "\" & GetBaseName(strSQLFile), csvText, "csv" ' Generate CSV file
Next
' 4. Disconnect from the DB
CloseDB objAdoCon
Set objAdoCon = Nothing
If DEBUG_MODE = 1 Then
WScript.Echo "Process completed."
End IfThis concludes the explanation. Using this sample as a base, you can easily implement tasks like extracting the latest logs from a table in the database every hour. For automated repetitive execution, consider using the Task Scheduler on Windows.